The water body is the living environment of fish, and its pH is the main indicator of fish pond water quality, which directly or indirectly affects the growth, development, reproduction and illness of fish. Fish are most suitable to grow in neutral or slightly alkaline water, that is, the pH value is 6.5-8.5. The most suitable pH value for fish growth is 7.8-8.5. When the pH value is 6-9, it is still within the safe range. If the pH value is below 6 or above 9, it will have adverse effects on fish.pH value is a comprehensive indicator of aquaculture water. The normal daily variation range of pH value in ponds is 1-2. If the PH value in the water body is too high, too low, or changes too much, it will affect the growth of aquatic organisms. During the breeding process of fish, if the pH value is too high or too low, it will not only cause the content of some chemical substances in the water to change, but even turn the chemical substances into toxic substances, which is detrimental to the growth of fish and the reproduction of plankton. It will inhibit photosynthesis, affect the dissolved oxygen status in the water, and prevent fish from breathing.
Practice has proved that under acidic (pH value lower than 5.5) conditions, fish in the water body are particularly sensitive to fish diseases and have difficulty breathing. Even if there is no lack of oxygen in the water, their feed digestibility is low and their growth is slow. In an acidic environment, the solubility of phosphate in the water body is affected, the decomposition rate of organic matter slows down, and the material circulation rate is slow, which affects the reproduction of bacteria, algae, and plankton. Moreover, fish gills will be corroded, making the fish’s blood more acidic, reducing the Oxygen-carrying capacity. Although the oxygen content in the water body is high, fish will still float, causing hypoxia. The activity of the fish will be weakened, the metabolism will slow down sharply, the food intake will be reduced, and the digestive capacity will be reduced, which is not conducive to the growth and development of the fish. At the same time, acidic water bodies can lead to a large number of fish diseases caused by protozoa, such as ciliate diseases. The pH value is between 5 and 6.5, which can easily lead to large-scale reproduction of dinoflagellates, which is also more harmful to fish. At low pH, the concentrations of Fe2+ ions and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) will increase, and the toxicity of these ingredients has a synergistic effect with low pH. The lower the pH, the greater the toxicity.
In the nitrogen cycle, pH value also plays an important role. For nitrification and nitrogen fixation, a weakly alkaline pH value of 7.5-8.5 is most suitable. High pH increases ammonia’s toxicity. pH value also indirectly affects fish growth by affecting other environmental factors. pH value also seriously affects the biological productivity of water bodies. Inappropriate pH value will destroy the most important material basis for water production – the supply of phosphate and inorganic nitrogen compounds. If the pond water is too alkaline, it will form insoluble calcium phosphate, and if it is too acidic, it will form insoluble iron phosphate and aluminum phosphate, which will reduce the fertilizer efficiency. It is not easy to fatten when cultivating water. It may be because the water body is too acidic.
Under normal circumstances, when the sun comes out, the pH value begins to gradually rise to the maximum value around 17:30 in the afternoon, and then begins to decrease until it reaches the minimum value before the sun comes out the next day. This cycle repeats, and the daily variation range of the pH value is 1.0-2.0. If it exceeds this range, there is something abnormal in the water body.
The causes, hazards and treatment methods of abnormal pH value;
- The pH value is too high or too high (alkaline water)
Symptoms of alkalosis in fish: irritation and weakened vitality; corroded gill covers, secretion of a large amount of mucus in the gills, and even the water body is alkaline, generally with a pH value greater than 9; there are many dead algae and dying algae cells in the water body.
If the pH value is too high or rises too fast, the ammonia nitrogen in the water body will be converted into molecular ammonia, and the toxicity will be doubled, especially when the pH value reaches above 10; algae blooms are easy to form in water bodies with high pH value; too high pH value is harmful to fish. The gills, skin and mucus are corrosive, causing the fish to secrete a large amount of mucus, which affects breathing.
- The pH value is low or too low (acidic water)
Symptoms of acidosis in fish: The body surface appears white; aquatic plants appear brown or white; the transparency of the water body increases significantly; the water body is acidic, generally with a pH value less than 4; there are many dead algae and dying algae cells in the water body. A pH value that is too low or drops too sharply is usually a comprehensive reflection of deterioration of water quality, reduction of dissolved oxygen in the water body, and an increase in harmful substances such as hydrogen sulfide. If the pH value is too low or drops too much, it will reduce and weaken the oxygen-carrying capacity of aquatic animals, cause tissue hypoxia, weaken fish activity, reduce metabolism, reduce food intake, slow growth, and also reduce the solubility of phosphate in the water body. , which in turn leads to weakened reproduction of phytoplankton, reduced decomposition rate of organic matter, and fish in acidic water bodies are more susceptible to parasitic diseases.

How to prevent and cure it?
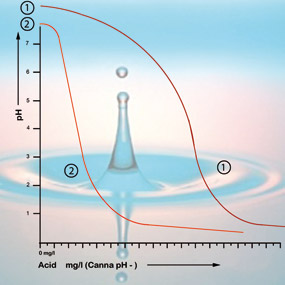
- The pH value is high. Use hydrochloric acid: Sprinkle hydrochloric acid in the whole pond according to the pH value. Use 300-500 ml per mu. It must be fully diluted and then poured into the whole pond to avoid local acidosis. Use talcum powder: The dosage is 2-4 pounds per mu. Spraying it in the whole pond can reduce the PH value of the water by 0.5-1.
- The pH value is low. Adjusting with quicklime works well. Use 20-30 kilograms of quicklime per mu each time, increasing or decreasing the amount according to the pH value (it can be as high as 60 kilograms per mu). Adjust with sodium hydroxide. When applying, pay attention to small amounts and multiple times. Method: first prepare a 1% stock solution, then dilute it with 1000 times of water, then add water while splashing, and measure the pH value of the water in time to avoid causing local alkalosis.
- Combined with sensors for real-time monitoring.
